

An In-situ Raman Electrochemical cell is a specialized setup designed for conducting Raman spectroscopy under controlled conditions, such as variable temperatures, pressures, chemical environments, or electrochemical processes. This allows researchers to observe real-time changes in materials or chemical processes without disturbing the sample environment.
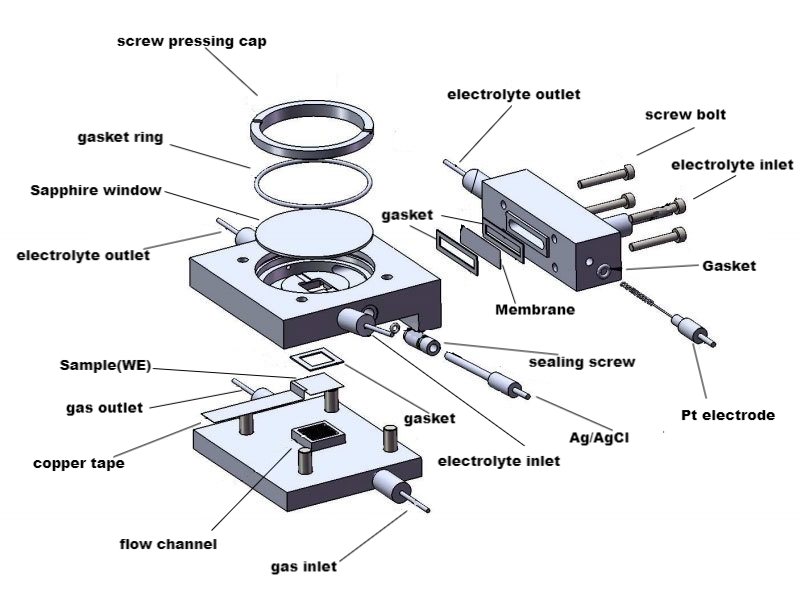
Key Features of an In-Situ Raman Cell:
u Transparent Windows:
Typically made of materials like quartz, sapphire, or glass, which are transparent to the laser wavelengths used in Raman spectroscopy.
u Controlled Environment:
•Temperature Control: Heaters or coolers to maintain specific sample temperatures.
•Pressure Control: Gas or liquid-tight cells can simulate high-pressure conditions.
•Atmosphere Control: Can introduce gases (e.g., inert gases, CO₂) or liquids to observe reactions.
u Electrochemical Compatibility (for electrochemical in-situ cells):
Electrodes are integrated into the cell to allow in-situ Raman analysis of electrochemical reactions, such as battery testing, fuel cells, or corrosion studies.
u Compact Design:
Optimized for fitting under the microscope of a Raman spectrometer while allowing access for lasers and detectors.
Applications of In-Situ Raman Cells:
u Catalysis Studies:
Monitor reaction intermediates and products under high temperatures and pressures.
u Battery and Energy Storage:
Real-time tracking of chemical changes in electrodes and electrolytes during charge/discharge cycles.
u Phase Transition Studies:
Analyze materials undergoing phase changes (e.g., solids to liquids) due to temperature or pressure variations.
u Corrosion Analysis:
Investigate corrosion mechanisms and the formation of corrosion products in real-time.
u Gas-Solid Reactions:
Study how gases interact with solid surfaces, such as in heterogeneous catalysis.
u Material Characterization:
Evaluate properties of new materials like 2D materials, polymers, and nanostructures.
Advantages of In-Situ Raman Cells:
u Provides real-time insights into dynamic processes.
u Allows studies under realistic operating conditions.
u Maintains sample integrity during analysis.